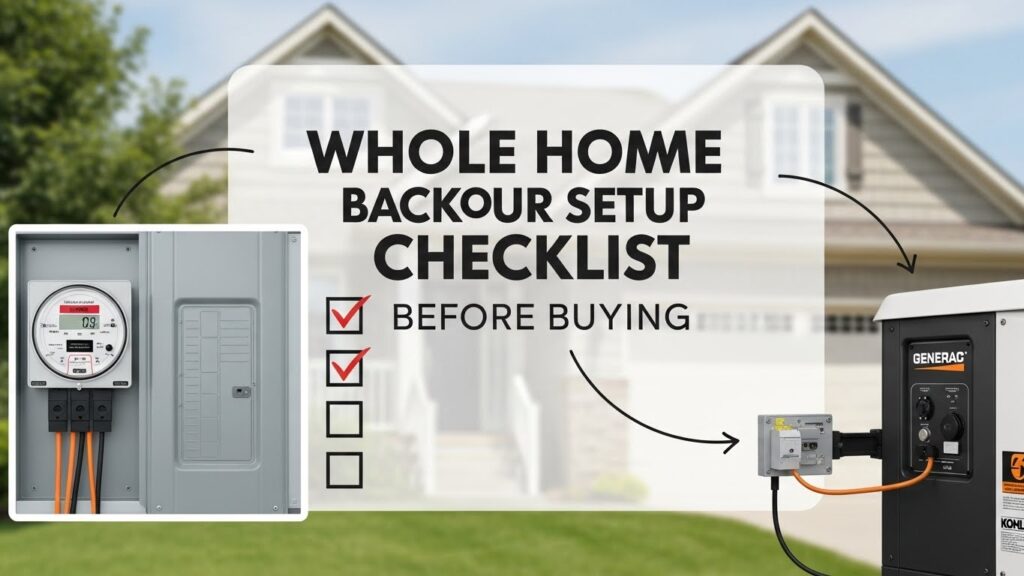
Whole Home Backup Power Setup Checklist Before Buying
Before making a purchasing choice for whole-house backup power, proper preparation is required. Homeowners must comprehend their electrical setup, area, and daily power requirements. Purchasing the wrong system results in a wasted expenditure or poor performance during outages. This checklist shows things to consider at home before choosing a whole-house backup power system. It addresses electrical capacity, appliance priority, space limitations, and future requirements. With proper planning, homeowners may select systems that are appropriate for their houses, prevent surprises, and acquire dependable backup power that works as expected when grid outages disturb regular living unexpectedly and frequently over time for safety, comfort, and stability.

What Should You Check at Home Before Buying Backup Power?
Assessing Electrical Panel Capacity and Service Size
Before purchasing backup power, you should first assess the capability of your electrical panel and the size of your service. Installers inspect the main panel’s rating, available breaker space, and service amperage. Many residences have 100A or 200A service, which limits system compatibility. Backup systems must integrate properly and without overloading circuits. Older panels may require updates to accommodate whole-home configurations. Homeowners should take heed of significant loads like HVAC systems or EV chargers. Accurate panel evaluation saves future delays, inspection difficulties, and unforeseen expenses. This stage ensures that the chosen system attaches properly, satisfies code, and provides reliable electricity without posing safety issues during outages or future house repairs or expansions.
Identifying Essential Appliances and Total Power Needs
Identifying important appliances and overall power requirements aids in determining the optimal backup configuration. Homeowners make a list of equipment they wish to be powered during outages. Refrigerators, medical equipment, internet routers, lights, and heating or cooling systems are all common essentials. Non-essential loads may include entertainment systems or supplementary appliances. Each appliance has a wattage rating that indicates demand. Adding these figures yields total power requirements. This method protects the system from being oversized or undersized. Clear priorities provide improved load management and increased runtime during disruptions. Knowing real demand enables households to select cost-effective solutions that support safety, comfort, and daily routines without incurring excessive expenses or compromises.
Evaluating Space, Clearances, and Placement Options
Evaluating space, clearances, and placement choices helps to avoid future installation issues. Backup power systems require sufficient circulation, access, and a safe distance from walls, windows, and vents. Outdoor equipment must follow local clearance regulations. Indoor battery systems require wall space and ventilation. Noise issues are equally important in residential environments. Tight confines restrict system capacity and expansion possibilities. Homeowners should measure the available space and take note of any impediments. Early planning saves money on relocation and inspections. Proper placement promotes safe operation, ease of maintenance, and long-term reliability while adhering to property limits and neighborhood safety and compliance needs for years of usage throughout outages and normal operating cycles.

How Do You Choose the Right Whole Home Backup Power Setup?
Standby Generators vs Battery Backup Systems
Standby generators and battery backup systems have different operations and applications. Generators operate on gasoline and offer continuous electricity during extended outages. They can withstand heavy loads but produce noise and pollutants. Battery systems store energy and deliver it discreetly. They activate instantaneously and are suitable for short to medium-term outages. Batteries work nicely with solar panels. The choice between them is determined by the length of the outage, noise tolerance, fuel availability, and budget. Homeowners should weigh maintenance requirements and installation difficulties. Understanding these distinctions enables purchasers to pick a dependable arrangement that is linked with their lifestyle demands and energy objectives, avoiding unnecessary compromise or future regret due to poor system matching selections made later in ownership.
Fuel Availability, Runtime, and Local Supply Reliability
Backup power performance is influenced by fuel availability, runtime, and the dependability of the local supply. Standby generators run on natural gas, propane, or diesel. Natural gas has a long duration when pipes are operating. Propane and diesel require stored fuel and refills. Supply interruptions have an impact on reliability during catastrophes. Battery systems do not use gasoline but rely on stored energy capacity. Solar charging can increase runtime. Homeowners should think about gasoline access during crises and local rules. Matching fuel type with area circumstances enhances system reliability. Planning fuel or energy availability guarantees that backup power is available when it is most required, without interruption or risky refilling operations during severe outages or long-term grid breakdowns.
Sizing the System to Match Current and Future Needs
Sizing the system to match current and future needs prevents early replacement. Homeowners consider present loads and planned upgrades. Electric vehicles, heat pumps, and home offices increase demand over time. Choosing scalable systems, such as a home battery backup, allows expansion later. Proper size strikes a balance between cost and capability. Oversized systems lose money, whereas undersized ones reduce performance. Professional evaluations assist in precisely matching capabilities. Planning ahead guarantees that backup power can accommodate lifestyle changes without requiring big changes. A properly sized system provides dependable performance across shifting demands and outage scenarios without stress or disturbance to daily routines or safety standards for residents worldwide today and in the future.
Conclusion
Before purchasing a whole-house backup power arrangement, it is important to carefully consider your options. Checking electrical capacity, appliance demands, and space helps to avoid costly mistakes. Comparing system types and fuel options reveals what works best. Proper size guarantees consistent performance now and flexibility tomorrow. Preparation minimizes delays and installation concerns. Homeowners who adhere to a defined checklist select solutions that interact seamlessly. Backup power thus becomes an essential component of the home. With the proper configuration, outages generate less inconvenience and stress. Planning ahead of time provides confidence, safety, and comfort when grid electricity goes out suddenly due to storms, heat waves, or infrastructure issues that disrupt everyday life.