Introduction
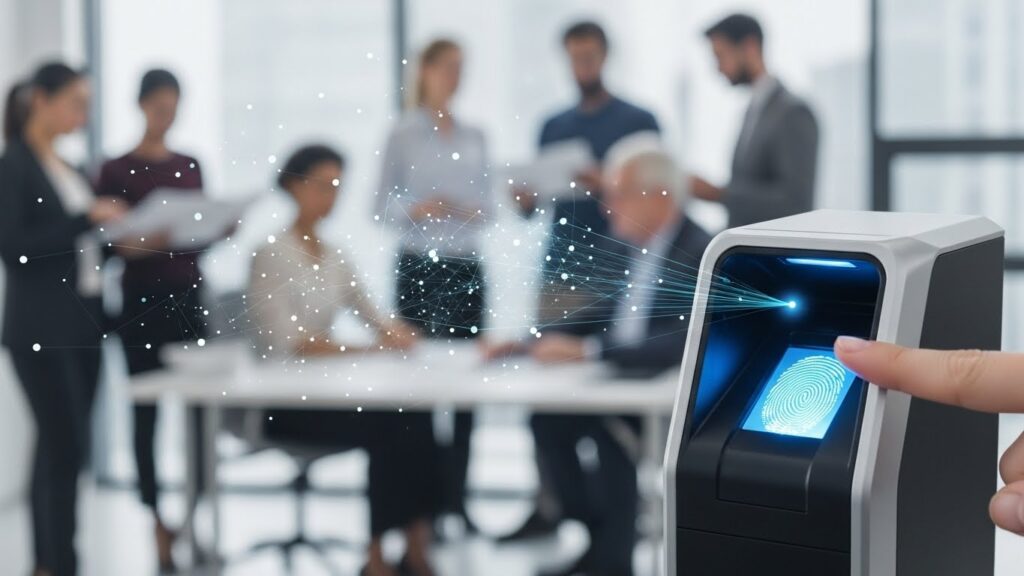
As organizations grow in complexity and face ever-evolving security threats, safeguarding people, assets, and sensitive data in the workplace has become an absolute necessity. One of the most effective ways companies accomplish this is through the implementation of fingerprint background check systems, which have emerged as a trusted method for verifying identities and flagging potential risks before they can impact business operations.
Unlike traditional background checks that rely on documentation or name-based searches, fingerprint checks use biometric data—unique to each individual—offering a reliable solution to prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and create peace of mind for employers and their teams. As the need for comprehensive safety protocols grows, the use of fingerprinting stands out in its ability to uncover criminal histories and reduce the potential for insider threats.
Fingerprint background checks aren’t only about eliminating risk; they reassure stakeholders, clients, and the wider community that an organization is upholding the highest standards of due diligence in its hiring and access management processes. These checks are especially crucial for businesses entrusted with sensitive information or serving at-risk or vulnerable populations, as they guard against negligent hiring and bolster public trust.
In addition, as regulations surrounding data privacy and workplace safety continue to increase, organizations require systems that deliver both security and compliance. Fingerprint checks, with their technological sophistication and accuracy, are positioned at the intersection of these goals, providing a secure and efficient screening tool that also respects individuals’ rights.
 Importance of Fingerprint Checks
Importance of Fingerprint Checks
The unique nature of fingerprints makes them one of the most reliable methods for authenticating someone’s identity, significantly reducing the risk of impersonation. By incorporating biometric analysis, employers can match job applicants or contractors with official records, revealing relevant criminal histories that may not be disclosed through self-reported information.
These enhanced screening capabilities protect workplaces on several fronts:
- Accurate Identification: A fingerprint scan provides proof that the background check accurately reflects the candidate’s true identity, closing loopholes common in paper-based vetting systems.
- Comprehensive Criminal History: Many law enforcement and federal background checks require fingerprints to access complete databases, which results in a wider and more up-to-date search than name-based versions.
- Enhanced Security: Continual verification through periodic checks reduces the risk of future breaches posed by evolving criminal activities.
Implementation in Various Industries
The application of fingerprint background checks varies according to industry, with certain sectors making their use mandatory due to regulatory and liability pressures:
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics must ensure care providers do not have disqualifying convictions, especially those related to abuse or theft, to protect patients and comply with healthcare regulations.
- Education: From early childhood through higher education, academic institutions use fingerprint checks to protect students, especially minors, from potential abuse or misconduct.
- Finance: Banks and financial service providers implement strict screening to prevent fraud, uphold industry standards such as the Bank Secrecy Act, and deter employees with histories of embezzlement or identity theft.
In addition to regulated industries, companies in logistics, government agencies, and security contractors also rely on fingerprint vetting to maintain high standards of trust and responsibility in their workforce.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
As fingerprint background checks collect and process biometric identifiers, organizations must be vigilant in upholding privacy and legal standards. Gathering fingerprints requires explicit, informed consent from candidates or employees. Employers have an obligation to explain how this data will be used, stored, and protected, ensuring compliance with rules such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for global organizations and state-specific laws like the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA).
To address these concerns, organizations invest in secure data management practices, implement clear consent protocols, and establish transparent dispute resolution pathways in cases of record errors or objections. Balancing security enhancements with ethical hiring standards remains a top priority, ensuring the prevention of discrimination and misuse of personal data.
Challenges and Solutions
Adopting fingerprint screening measures can present logistical and technological hurdles. Data security is arguably the biggest challenge, as biometric data, if breached, is irreversible and susceptible to misuse. Organizations must invest in encrypted storage solutions, restrict internal access, and regularly audit their systems for vulnerabilities.
There are also concerns about accuracy, including the potential for false positives or negatives that could lead to misidentification. To overcome these issues, companies should select screening vendors that conduct frequent system updates and maintain the highest accuracy rates in their fingerprint analysis algorithms.
Lastly, implementation costs, such as equipment purchase or integration with HR platforms, may seem prohibitive at first. However, evidence shows that the long-term benefits, including reduced turnover, legal protection, and enhanced workplace reputation, more than justify the initial investment.
Future Trends in Fingerprint Background Checks
As digital transformation accelerates worldwide, fingerprint background checks are poised to become more accessible and sophisticated. Major trends driving change include:
- Integration with Digital Identity Verification: Linking fingerprint scans to secure digital identities enables remote credential verification and streamlines onboarding processes for distributed teams.
- Advancements in Technology: Enhanced recognition algorithms, mobile fingerprint capture, and AI-driven background scoring allow for faster, more reliable screening with minimal human error.
- Increased Adoption: As security threats diversify, industries such as transportation, hospitality, and gig economy platforms are expanding the use of biometric checks for both staff and contractors.
The shift towards frictionless, real-time background checks is not only improving operational efficiency but is also changing expectations for trust and safety in the digital workplace.
Final Thoughts
Fingerprint background checks are a pivotal part of workplace due diligence in our digital era. By accurately verifying identities and flagging potential risks, they sustain the trust, safety, and compliance required of responsible organizations. As these technologies evolve and integrate more deeply into the fabric of talent acquisition and security procedures, their role in safeguarding employees and reputations will only grow in significance.