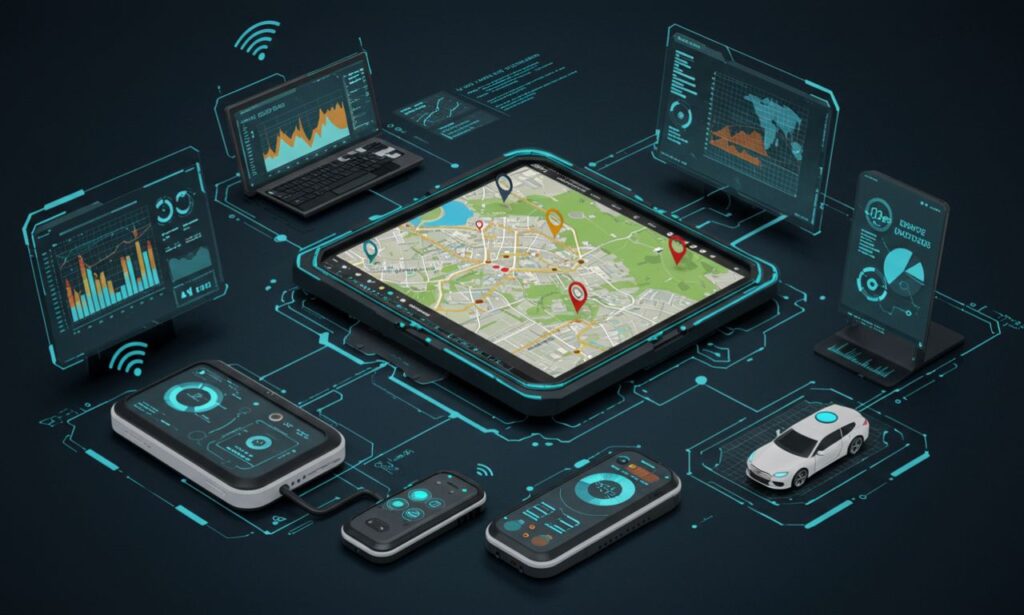
In an age where real-time data powers decision-making, the term “telemetryczny” (Polish for telemetric) is becoming increasingly important across industries. Whether it’s tracking a patient’s vital signs remotely or monitoring vehicle performance in real time, telemetric systems—or systemy telemetryczne—are changing the way we measure, manage, and respond to information.
This article explains what telemetryczny means, how telemetric systems work, and where this technology is having the biggest impact in today’s connected world.
What Does “Telemetryczny” Mean?
The word “telemetryczny” is an adjective derived from “telemetria”, which means telemetry—the process of collecting and transmitting data from remote or inaccessible locations to a central system for analysis and monitoring.
A telemetryczny system refers to any setup that includes:
-
Sensors to collect real-world data (e.g., temperature, pressure, motion)
-
Transmitters to send the data wirelessly or through networks
-
Receiving and processing units to analyze the data and make it actionable
How Do Telemetryczny Systems Work?
-
Data Collection
A telemetryczny system starts with sensors that collect specific data points—such as a car’s speed, a heart monitor’s ECG data, or the energy output of a solar panel. -
Wireless Transmission
The data is then sent to a remote server or device using communication technologies like cellular networks, Wi-Fi, satellite, or radio frequency (RF). -
Data Processing and Analysis
The received data is stored and analyzed using specialized software, often visualized on dashboards or integrated into automated systems. -
Real-Time Feedback
The system can then trigger alerts, updates, or adjustments based on pre-set thresholds—helping users or machines respond in real time.
Applications of Telemetryczny Systems
Telemetry technology is deeply embedded in today’s connected ecosystem. Here are some of the most common use cases for telemetryczny solutions:
1. Healthcare (Telemedicine)
Telemetryczny equipment in hospitals and homes allows doctors to monitor patients’ heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and other vital signs remotely.
-
Benefits: Early detection of issues, reduced hospital visits, and real-time emergency alerts.
2. Automotive and Fleet Management
Vehicles use telemetric data to monitor fuel usage, engine diagnostics, driving behavior, and GPS tracking.
-
Benefits: Optimized routes, predictive maintenance, improved safety.
3. Energy and Utilities
Telemetryczny meters and systems track electricity, water, or gas usage and send data back to providers for billing and load management.
-
Benefits: Accurate consumption data, reduced outages, remote troubleshooting.
4. Industrial and Manufacturing Systems
Machines fitted with telemetry sensors send operational data to central control rooms.
-
Benefits: Predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, enhanced process control.
5. Aerospace and Defense
Telemetryczny systems are critical in monitoring the condition of aircraft, spacecraft, and weapons systems—especially when human presence is not possible.
-
Benefits: Mission safety, real-time status monitoring, failure detection.
The Rise of IoT and Smart Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) has pushed telemetry from specialized industries into everyday life. Smart homes, wearables, connected appliances, and fitness trackers all rely on telemetryczny technologies to function.
For example:
-
A smartwatch collects your heart rate and sleep data.
-
It transmits that data to your phone.
-
The phone’s app visualizes trends and gives recommendations.
-
That entire process is powered by a telemetric (telemetryczny) system.
Key Technologies in Telemetryczny Systems
-
Sensors: Temperature, pressure, motion, biochemical, GPS
-
Data Transmission: 4G/5G, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, Satellite
-
Cloud Infrastructure: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud for real-time data processing
-
AI & Machine Learning: To predict trends, detect anomalies, and improve efficiency
-
Security Protocols: End-to-end encryption, authentication layers, and compliance standards (GDPR, HIPAA)
Challenges in Telemetryczny Implementations
While telemetry is powerful, implementing a telemetryczny system comes with some challenges:
-
Data Privacy and Security: Sensitive data, especially in healthcare, must be protected.
-
Connectivity Issues: Remote areas may lack stable network access.
-
Battery Life: Devices often need to operate for long periods without charging.
-
Data Overload: Managing and analyzing huge volumes of data can be overwhelming without proper systems.
Future of Telemetryczny Technologies
As 5G networks, edge computing, and AI continue to evolve, telemetryczny systems will become faster, more reliable, and more intelligent. We’ll see:
-
Real-time health diagnostics integrated into national healthcare systems
-
Smart cities use telemetry for traffic, air quality, and waste management
-
Autonomous vehicles rely on telemetric systems to make driving decisions
-
Enhanced predictive maintenance in factories and infrastructure
Final Thoughts
The word “telemetryczny” may sound technical, but its impact is deeply woven into our daily lives. From the way we track our health to how cities manage energy and traffic, telemetric systems are revolutionizing the world by turning raw data into intelligent action.
As innovation continues to accelerate, expect telemetryczny solutions to play an even greater role in creating smarter, safer, and more efficient systems across every sector.