Introduction
Industrial adhesives are an integral component of modern manufacturing and construction, offering advanced solutions for bonding a wide range of materials and enabling innovation that traditional welding, screws, or rivets cannot match. Whether you’re assembling products on a factory floor or securing substrates for construction, selecting the right adhesive is critical for ensuring the durability, safety, and longevity of the finished product. The wrong adhesive can lead to structural failure, while the right one can streamline production and improve end-user satisfaction. With rapid advancements in chemistry and specialized formulations, options such as the NXT Level Packaging Hot Melt Adhesive offer innovation and reliable bonding for a growing range of applications. A well-informed decision on adhesive selection can significantly impact production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product performance.
From lightweight consumer packaging to the construction of complex assemblies in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace sectors, industrial adhesives enable versatile, high-strength bonds without the need for heavy mechanical fasteners. They make possible the lightweighting of vehicles, enhance the aesthetics of electronics, and contribute to the sustainability of modern infrastructure by reducing energy and resource consumption.
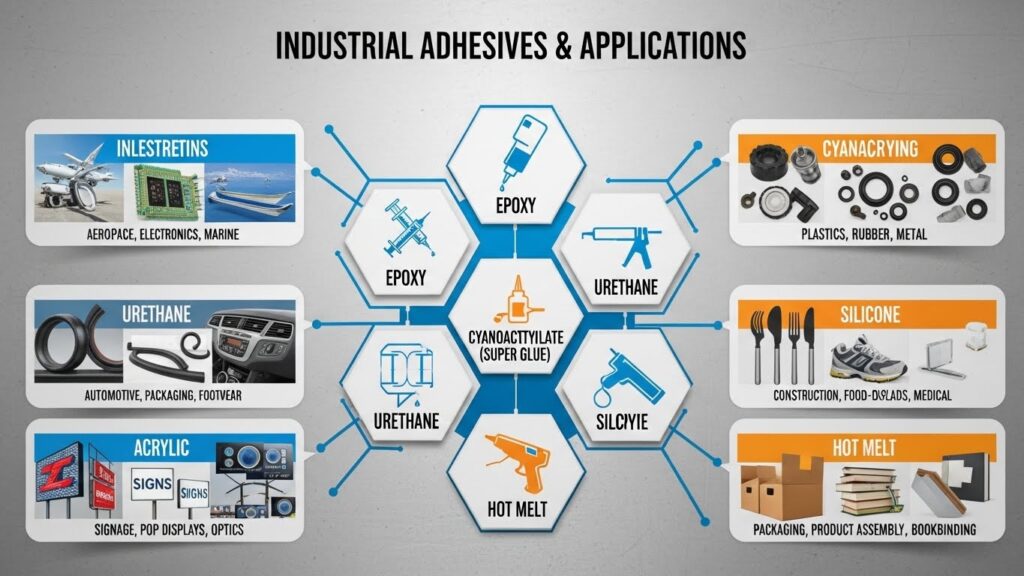
Hot-Melt Adhesives
Hot-melt adhesives (HMAs) are thermoplastic compounds that transition from a solid to a liquid when heated, bonding materials as they cool and solidify. These polymers typically consist of ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), polyamide, or polyolefin bases, each tailored for specific applications and performance profiles. Their rapid set times and strong adhesion make them indispensable in environments where speed, efficiency, and reliability are paramount, such as food and beverage packaging, bookbinding, woodworking, and furniture manufacturing. In the packaging industry, HMAs are routinely used for assembling and sealing cartons and boxes, forming a secure hold in just seconds—which is vital for high-volume production lines. Their versatility ensures that they play a significant role not only in packaging but also in product assembly lines, labeling, and even electronics encapsulation for water-resistant protection. HMAs also offer advantages like minimal waste, no need for solvents, and simplified equipment cleaning.
Epoxy Adhesives
Known for their exceptional bonding strength and unparalleled chemical resistance, epoxy adhesives are typically a two-component system consisting of a resin and a hardener. When mixed, these components react to form a tough, durable thermoset polymer that develops robust bonds even in extreme environments. Epoxies are a preferred choice in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial construction sectors for applications requiring high structural integrity, such as assembling engine parts, mounting brackets, repairing composite material, or reinforcing concrete structures and steel supports. Their ability to securely bond metals, composites, glass, ceramics, wood, and some plastics makes them remarkably adaptable. Additionally, epoxy adhesives withstand wide temperature swings, intense vibration, harsh chemicals, and heavy mechanical loads. Their gap-filling properties make them an essential tool for repairing worn machinery or anchoring bolts into heavy-duty surfaces, and they are often selected for electrical potting and encapsulation for critical circuit boards.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as super glues, are prized for their fast-curing capabilities and are ideal for applications requiring quick, strong bonds in seconds. These adhesives work by polymerizing in the presence of water vapor (humidity) in the air, making them particularly valuable for swift repairs and instant assembly in industries such as electronics, precision tooling, and medical device assembly. Their major advantage lies in their versatility—they can bond a variety of substrates, including plastics, rubber, metals, and even some porous materials like paper and wood. Due to their low viscosity and capillary action, they can easily penetrate small cracks and seams, making them effective for bonding tight-fitting parts and assembling miniature components. However, cyanoacrylates have certain limitations: they perform best in applications where flexibility and moisture resistance aren’t as critical. Prolonged exposure to moisture or dynamic stress can eventually weaken the bond, and thermal stability may be limited compared to epoxies or silicones.
Polyurethane Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives are renowned for their exceptional elasticity and ability to form strong bonds between dissimilar substrates, including wood, metal, glass, ceramics, and composites. Widely used in the automotive and construction industries, these adhesives are particularly effective for structural bonding, waterproof sealing, and vibration dampening. In automotive manufacturing, polyurethane adhesives are often used for windshield installation due to their ability to absorb impacts and withstand temperature fluctuations. In construction, they are valued for their use in flooring systems, panel assembly, and architectural joint sealing, where both strength and flexibility are essential. Their chemical composition also makes them resistant to moisture, chemicals, and environmental stressors, allowing their use in marine applications, outdoor construction, and heavy-duty repairs.
Polyurethane adhesives cure via a reaction with atmospheric or substrate moisture, ensuring strong performance even when bonding challenging surfaces. For businesses seeking to enhance product assembly or packaging processes, selecting polyurethane adhesives can lead to increased productivity, reduced rework, and cost savings compared to mechanical fasteners.
Silicone Adhesives
Silicone adhesives are unique for their ability to maintain elasticity and adhesion across a broad temperature range from sub-zero conditions to extreme heat. These adhesives are crucial in industries where components must remain flexible despite environmental stresses. Used extensively for sealing and insulating electronic components, silicones prevent moisture ingress and electrical shorts. In the construction sector, they are favored for weatherproofing tasks like window glazing, roof flashing, and facade joint sealing, where movements due to temperature changes and UV exposure are frequent. Unlike rigid adhesives, silicone remains flexible, accommodating movement and settling without losing adhesion—a critical advantage in high-stress assemblies. Their chemical inertness and stability also make silicones the adhesive of choice in medical devices, pharmaceutical packaging, and food-processing equipment where standards of cleanliness and biocompatibility must be met.
Acrylic Adhesives
Acrylic adhesives are renowned for their rapid curing times, structural strength, and exceptional durability against aging and weathering. Used widely in automotive and transportation manufacturing for bonding decorative trims, panels, emblems, and even composite assemblies, these adhesives are also popular in signage, electronics, HVAC systems, and construction. Acrylics form strong bonds to metals and plastics, and they also tolerate oily or slightly dirty surfaces, reducing the need for extensive surface preparation. Their high resistance to UV radiation and environmental degradation makes them ideal for outdoor and high-visibility components where appearance and bond strength must be preserved over time. Additionally, the adaptability of acrylic adhesives to automated production environments, including precision dispensing and spray applications, ensures their prominence in contemporary industrial manufacturing. The ease of use, combined with excellent bonding capabilities and weather resistance, often positions acrylic adhesives as a preferred choice for businesses seeking long-lasting, low-maintenance solutions.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right industrial adhesive has a direct impact on the overall quality, safety, and lifespan of your finished products, with significant implications for both manufacturing efficiency and cost control. Elements such as material compatibility, environmental conditions, curing time, and specified bond strength must be carefully considered during the selection process to prevent failure or additional maintenance costs in the future. By understanding the unique properties and advantages of each adhesive type, manufacturers and engineers can optimize assembly processes, increase product reliability, and ensure compliance with safety and industry standards in every application. Proper selection and application of adhesives not only enhance productivity but also contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing material waste and resource consumption. When faced with complex bonding challenges, consult with a materials specialist or adhesive supplier to determine the optimal adhesive formulation for your project’s specific requirements and ensure superior long-term performance in your applications.