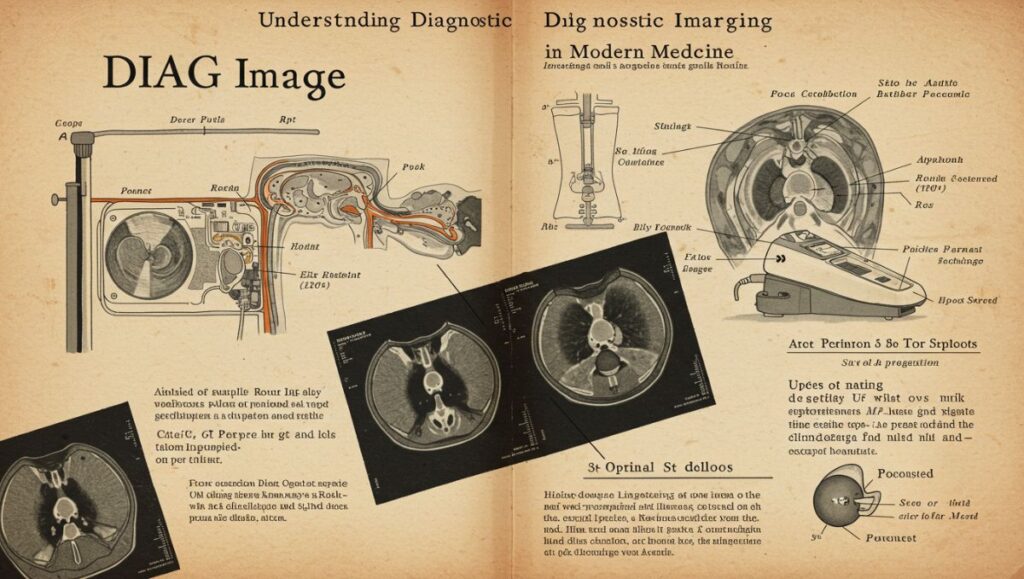
Diagnostic imaging, often shortened to DIAG image in clinical settings, plays a critical role in the early detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of diseases. From X-rays to MRI scans, DIAG images offer medical professionals a non-invasive view of the body’s internal structures, allowing for timely and accurate treatment decisions.
What Is a DIAG Image?
A DIAG image refers to any visual representation produced using diagnostic imaging technologies. These images help doctors visualize bones, tissues, organs, and other internal systems without surgical intervention.
Common types of diagnostic imaging include:
-
X-rays
-
Computed Tomography (CT) scans
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
-
Ultrasound
-
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans
-
Mammography
Each method produces a specific type of DIAG image suited to different diagnostic needs.
Types of DIAG Image Techniques
1. X-Ray Imaging
X-rays are the most common and oldest form of diagnostic imaging. They are typically used to detect:
-
Bone fractures
-
Infections (like pneumonia)
-
Dental issues
-
Joint abnormalities
X-rays use a small amount of ionizing radiation to produce images and are quick, painless, and widely accessible.
2. CT Scans
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan takes multiple X-ray images from different angles and compiles them into cross-sectional views. CT DIAG images are used for:
-
Detecting tumors
-
Evaluating trauma or internal injuries
-
Guiding biopsies and surgeries
CT scans offer more detail than standard X-rays and can image soft tissues, blood vessels, and bones simultaneously.
3. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed DIAG images, especially of soft tissues. It is commonly used for:
-
Brain and spinal cord examinations
-
Joint injuries
-
Ligament or tendon damage
-
Tumor detection
Unlike X-rays and CTs, MRI doesn’t use ionizing radiation, making it safer for certain patients.
4. Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time DIAG images. It’s most commonly associated with:
-
Pregnancy monitoring
-
Abdominal organ evaluations
-
Blood flow analysis
-
Guiding needle biopsies
Ultrasound is portable, radiation-free, and ideal for soft tissue imaging.
5. PET Scans
A PET scan provides functional DIAG images by showing how tissues and organs are working, not just how they look. It is often combined with CT for cancer staging and monitoring.
Why Are DIAG Images So Important?
DIAG images allow healthcare professionals to:
-
Detect diseases early before symptoms appear
-
Confirm a diagnosis after physical exams or lab tests
-
Monitor disease progression or treatment effectiveness
-
Guide surgical procedures or biopsies
-
Avoid unnecessary surgeries through accurate visualization
They reduce the need for exploratory surgery and help ensure that treatment plans are based on solid evidence.
The Process of Creating a DIAG Image
Each imaging method has its protocol, but the general process includes:
-
Patient Preparation: May include fasting, changing into medical gowns, or removing metal objects.
-
Image Capture: Using specialized machines operated by trained technicians (radiologic technologists).
-
Image Analysis: A radiologist or physician interprets the DIAG image to identify abnormalities or patterns.
-
Reporting: Results are compiled into a report and sent to the referring doctor for further action.
The entire process can take minutes (like in X-rays) or up to an hour or more (as in complex MRIs or PET scans).
Who Performs and Interprets DIAG Images?
Radiologic Technologists
These healthcare professionals are trained to operate imaging machines and ensure accurate, safe image acquisition.
Radiologists
Radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in interpreting DIAG images. They work with other healthcare providers to make diagnostic and treatment decisions.
Advantages of DIAG Imaging
-
Non-invasive: Offers a way to “see inside” without surgery
-
Early detection: Identifies diseases before symptoms become severe
-
Precision: Helps target treatment to the exact area of concern
-
Speed: Many imaging methods are fast and yield immediate results
-
Cost-effective: Reduces guesswork and unnecessary procedures
Limitations and Risks of DIAG Imaging
While powerful, DIAG images have some limitations:
-
Radiation exposure: Particularly from X-rays and CT scans (though kept minimal)
-
Cost: MRI and PET scans can be expensive without insurance
-
Availability: Not all facilities have advanced imaging equipment
-
False positives/negatives: Sometimes images may miss issues or flag benign conditions as suspicious
The Future of DIAG Imaging
Technology in medical imaging continues to evolve rapidly. Emerging trends include:
1. AI-Assisted Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being used to analyze DIAG images with high speed and accuracy. AI can detect subtle patterns and reduce human error.
2. 3D and 4D Imaging
Advanced imaging now allows for 3D reconstructions and even 4D imaging (real-time 3D), enhancing surgical planning and diagnostics.
3. Portable Imaging Devices
Smaller, mobile imaging tools are making it possible to bring diagnostic tools directly to patients, even in remote or rural areas.
4. Personalized Imaging
Using genetics and other patient data, future DIAG images may be customized to reveal how specific diseases might affect individuals differently.
Conclusion
DIAG images are a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics. They allow doctors to detect, diagnose, and monitor conditions with precision and confidence. Whether it’s a simple chest X-ray or a complex MRI brain scan, DIAG imaging helps guide patient care every step of the way.
As technology advances, DIAG images will become even more accurate, accessible, and integrated into daily healthcare. For patients and providers alike, diagnostic imaging continues to be an essential tool in the journey toward better health.