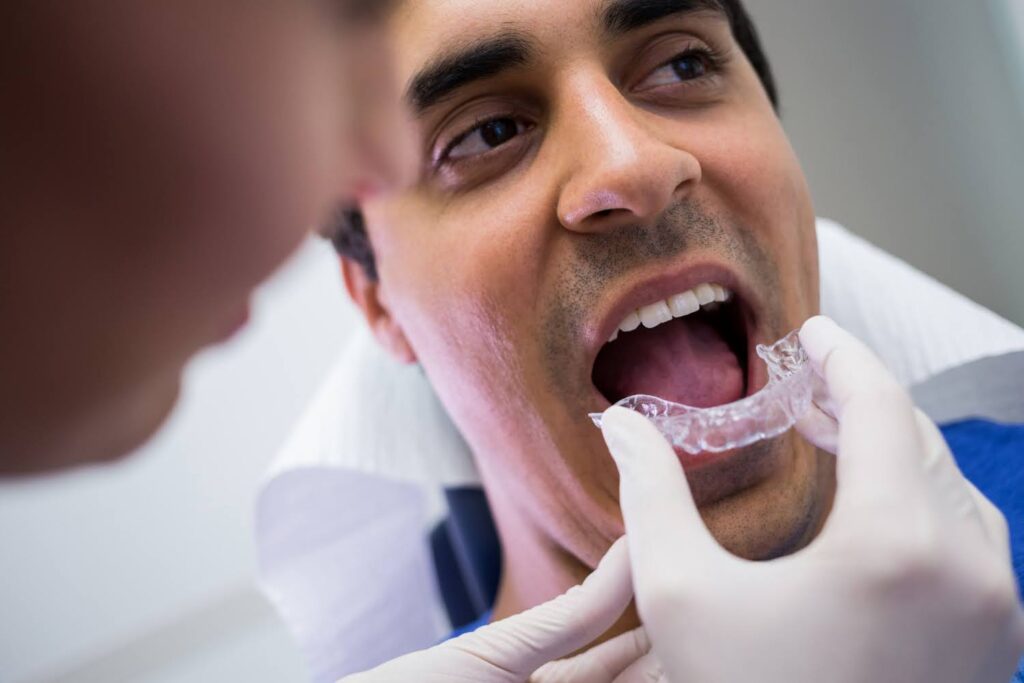
Dentistry has evolved far beyond the traditional metal and acrylic dentures that once defined removable prosthetics. Today, patients and clinicians seek solutions that combine strength, comfort, and natural aesthetics. Among these innovations, flexible partial dentures have emerged as one of the most significant developments in restorative dentistry. This evolution is rooted not just in design, but in the breakthroughs of material science that have transformed how dentists approach partial tooth replacement.
From Conventional to Contemporary Materials
For decades, metal frameworks and rigid acrylic bases dominated partial denture design. While these materials were durable, they often came with limitations: metal could cause allergic reactions, acrylic might feel bulky, and both could lead to sore spots or speech difficulties. The rise of flexible thermoplastic materials changed this equation completely. These modern polymers allow for thinner, lighter, and more adaptable dentures that can conform to each patient’s mouth.
This scientific shift toward flexibility is reshaping clinical practice. Dentists now have access to advanced materials that offer patients comfort without compromising functionality or durability. The change is so remarkable that flexible partial dentures are increasingly becoming the first choice for many partial denture cases where adaptability and aesthetics matter most.
How Material Science Changed the Clinical Workflow
Advancements in polymer chemistry have revolutionized how dentures are fabricated. Instead of relying on brittle acrylics, modern dentures are crafted from thermoplastic resins such as polyamide or nylon. These materials can be injection-molded under controlled heat and pressure, creating a base that is flexible yet strong enough to withstand chewing forces.
For clinicians, this innovation has simplified the process. There is less need for metal clasps or adjustments after delivery. The material’s natural elasticity allows it to grip the teeth and gums comfortably without exerting excessive pressure. This means fewer sore spots and adjustments for patients. The entire experience from lab fabrication to chairside fitting has become more efficient and patient-friendly.
Improved Comfort and Aesthetics for Patients
Material advancements have not only benefited clinicians but also transformed patient satisfaction. Flexible dentures offer a translucent base that blends seamlessly with the natural color of the gums. The improved flexibility helps reduce friction and irritation on soft tissues, especially in patients with uneven ridges or sensitive mucosa.
Another important benefit is the reduction of allergic reactions. Traditional denture materials sometimes contained residual monomers or metals that could cause sensitivities. The new generation of thermoplastic materials is biocompatible and hypoallergenic, ensuring safety for a wider range of patients.
Flexible dentures demonstrate how modern materials are reshaping patient outcomes. These innovations show that material flexibility directly enhances comfort and function without the need for rigid frameworks.
The Science Behind Strength and Durability
The flexibility of thermoplastic resins does not mean they are weak. Material scientists have worked to achieve an ideal balance between elasticity and resistance. By optimizing polymer chains and refining molecular structures, they have created dentures that can endure long-term wear without deformation.
Modern thermoplastics also show lower water absorption rates, which prevents discoloration and odor buildup. This improvement addresses one of the biggest issues of older flexible materials. As a result, maintenance has become easier, and long-term performance has improved. For clinicians, it means fewer relines and replacements, and for patients, it means longer-lasting smiles.
Integrating Technology and Material Science
The digital revolution in dentistry has further supported the success of flexible materials. 3D scanning, CAD/CAM technology, and precision milling have allowed for more accurate fits and reduced fabrication time. These tools ensure that every denture aligns perfectly with the patient’s anatomy. When combined with thermoplastic materials, the outcome is a prosthesis that feels more natural and requires minimal adjustment.
This integration of digital workflows and advanced materials reflects the modern direction of prosthodontics: custom, patient-centered, and efficient. It marks the convergence of science and technology in everyday clinical practice.
A Future of Smarter, Softer Smiles
Looking ahead, researchers are developing materials that can subtly adjust to temperature or humidity, keeping dentures comfortable throughout the day. Nanotechnology and bioactive polymers are also showing promise in supporting gum health while maintaining long-term durability. The aim is to keep improving comfort, function, and a natural appearance through ongoing material innovation.
These advancements also reflect a move toward a more sustainable future in dentistry. With reduced material waste, better recyclability, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes, flexible denture materials are helping create a cleaner and more responsible dental industry. It’s a positive change that aligns with how modern dental care is evolving.
Revived Smiles continues to highlight how new ideas in material science can make dental solutions more comfortable, sustainable, and patient-centered than ever before.
Conclusion
The story of flexible dentures is, at its core, a story of material science catching up with human need. By focusing on comfort, biocompatibility, and aesthetic harmony, these advancements have redefined the standard of care for partial dentures. What began as an experiment in flexibility has grown into a full-fledged revolution in restorative dentistry.
As dental materials continue to evolve, one thing is clear: the next generation of dentures will not only fit better and look more natural but will also represent a perfect fusion of engineering, biology, and compassion in patient care.